
Orthodontics realized in Egypt is an effective treatment that one can benefit from it and at any age in order to correct misalignment, overlapping or protrusion of teeth that affect their appearance and function.
It is a widespread practice thanks to new treatment technologies and it does not only improve the smile and the harmony of the face, but also promotes good health as aligned teeth are easier to brush and therefore less prone to cavities.
The price of orthodontics in Egypt
The price orthodontics Egypt is affordable, so, if you want to have the cost orthodontics Egypt, ask for a free online quote or contact us by phone on our phone numbers that you will find on our website to be in touch with one of our counselors who will guide you and answer all your questions.
What are the types of the Orthodontics procedure ?
Orthognathic Surgery :
Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery, is a type of orthodontic surgery that aims to correct severe jaw abnormalities and misalignments that cannot be corrected with braces or other orthodontic treatments alone.
This procedure is typically performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons in collaboration with orthodontists. The goal of orthognathic surgery is to improve the function of the jaw and bite, as well as enhance facial aesthetics.
The process of orthognathic surgery begins with a comprehensive evaluation, including dental and facial imaging, to assess the extent of the jaw misalignment and plan the surgical procedure accordingly. Common conditions that may necessitate orthognathic surgery include underbites, overbites, open bites, crossbites, and asymmetry of the jaws.
During the surgery, the surgeon carefully cuts and repositions the jaw bones to achieve proper alignment and balance. This may involve repositioning the upper jaw (maxilla), lower jaw (mandible), or both, depending on the individual's specific needs. The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting and may require a brief hospital stay for recovery.
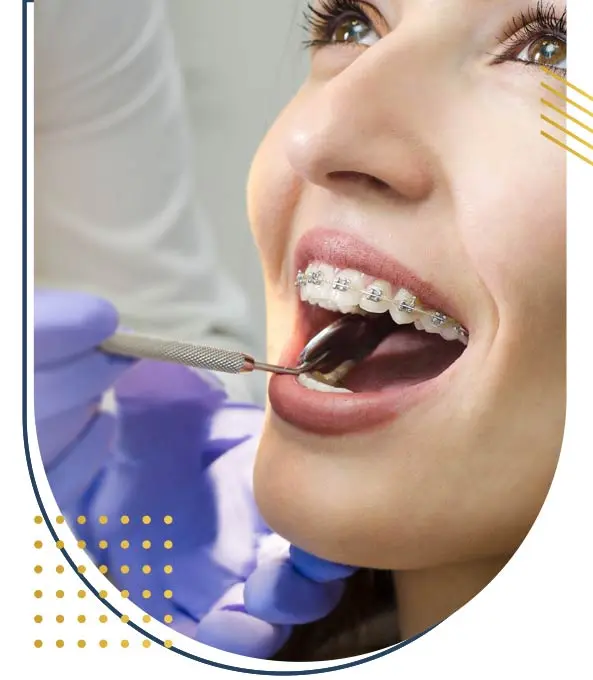
Distraction Osteogenesis :
Distraction osteogenesis is a surgical technique used to gradually lengthen or reshape bone tissue to correct skeletal deformities and deficiencies.
This innovative procedure has revolutionized the field of orthodontics, offering an alternative approach to traditional orthognathic surgery for certain conditions.
The process of distraction osteogenesis involves making a surgical incision near the site of the affected bone and inserting a device called a distractor. This device consists of two separate pieces connected by a screw mechanism.
Over a period of several weeks to months, the distractor is gradually adjusted to apply tension to the bone, stimulating new bone growth in the desired direction.
Distraction osteogenesis is particularly beneficial for patients with congenital abnormalities, such as cleft lip and palate, as well as individuals with severe jaw discrepancies or craniofacial syndromes.
Unlike traditional orthognathic surgery, which involves cutting and repositioning the bones in a single procedure, distraction osteogenesis allows for more controlled and gradual correction of skeletal deformities, reducing the risk of complications and improving outcomes.
One of the key advantages of distraction osteogenesis is its versatility and adaptability to a wide range of anatomical and clinical situations.
The technique can be applied to various bones throughout the body, including the jaws, facial bones, long bones of the limbs, and even the skull. This flexibility makes it a valuable tool in the treatment of complex craniofacial anomalies and other orthodontic conditions.
Alveolar Bone Grafting:
Alveolar bone grafting is a surgical procedure commonly performed in conjunction with orthodontic treatment to restore missing or deficient bone in the upper jaw (maxilla). This procedure is often necessary for individuals with cleft lip and palate or other congenital conditions that result in insufficient bone development in the oral cavity.
The alveolar bone is the ridge of bone that surrounds and supports the roots of the teeth. In patients with cleft lip and palate, the alveolar ridge may be incomplete or underdeveloped, leading to dental problems and difficulties with speech and chewing.
Alveolar bone grafting involves transplanting bone tissue from another part of the body, typically the hip or tibia, to augment the deficient area of the jaw.
The surgical technique for alveolar bone grafting varies depending on the specific needs of the patient and the extent of the bone deficiency.
In general, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting and may involve making an incision in the gum tissue to access the underlying bone. The transplanted bone graft is then secured in place and allowed to heal, integrating with the surrounding bone over time.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Surgery :
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) surgery is a specialized orthodontic procedure aimed at treating disorders and dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, which connects the jawbone to the skull. TMJ disorders can result from a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, teeth grinding, or malocclusion.
When conservative treatments such as medication, physical therapy, or splints fail to alleviate symptoms, surgery may be recommended to address underlying structural issues within the joint.
The surgical techniques used to treat TMJ disorders vary depending on the specific nature and severity of the condition.
Arthroscopic surgery, which involves inserting a small camera and surgical instruments through tiny incisions near the joint, may be utilized to diagnose and treat certain TMJ problems, such as disc displacement or inflammation. In more complex cases, open-joint surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joint structures, remove scar tissue, or reposition the jaw to improve function and alleviate pain.
TMJ surgery is typically performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons with expertise in treating disorders of the jaw and facial structures. Prior to surgery, patients undergo a comprehensive evaluation, including imaging studies and a thorough examination of jaw function and symptoms.
The surgical approach is tailored to the individual's specific needs and may involve a combination of techniques to achieve optimal outcomes.
Surgical Exposure of Impacted Teeth :
Surgical exposure of impacted teeth is a common orthodontic procedure performed to facilitate the eruption of teeth that are trapped beneath the gum line or bone tissue. Impacted teeth can occur for various reasons, including overcrowding, abnormal tooth development, or inadequate space in the dental arch.
If left untreated, impacted teeth can lead to complications such as infection, cyst formation, or misalignment of adjacent teeth.
The surgical exposure technique involves making an incision in the gum tissue and, if necessary, removing a small amount of bone to expose the impacted tooth beneath. In some cases, a bracket or orthodontic appliance may be attached to the exposed tooth to aid in its guided eruption into proper alignment.
Once the tooth has been exposed, orthodontic treatment such as braces or aligners may be used to guide it into its correct position within the dental arch.
Genioplasty :
Genioplasty, also known as chin surgery or mentoplasty, is a type of orthognathic surgery that focuses on reshaping and repositioning the chin to improve facial aesthetics and harmony.
This procedure is commonly performed in conjunction with other orthodontic treatments, such as orthognathic surgery or braces, to achieve optimal facial balance and proportion.
The chin plays a crucial role in defining the lower face and jawline, and abnormalities in chin position or size can significantly impact facial aesthetics.
Genioplasty allows for precise modification of the chin to address concerns such as a receding chin (retrogenia) or an overly prominent chin (prognathism), creating a more balanced and harmonious facial profile.
The process of genioplasty begins with a comprehensive evaluation, including facial analysis and imaging studies, to assess the patient's facial anatomy and develop a customized treatment plan. The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia by oral and maxillofacial surgeons with expertise in facial reconstruction and aesthetics.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes precise incisions in the jawbone to access the chin area and carefully repositions or reshapes the bone to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome. Depending on the specific goals of the surgery, the chin may be advanced, reduced, or augmented using techniques such as osteotomy (bone cutting) or implants.
Who can benefit from orthodontic treatment ?
Orthodontic treatment is for patients who suffer from problems related to articulation, chewing because of misaligned, overlaping or protruding teeth.
The position of the teeth and jaw can affect the occlusion. Occlusion refers to the articulation of the upper teeth with the lower ones. When the upper teeth are not well articulated with the lower teeth, it is called a dental malocclusion. Missing, misaligned, overlapping or protruding teeth can contribute to malocclusion.
Malocclusion can make it difficult to chew certain foods and can cause some teeth to wear down. It can also cause muscle tension and pain. Advanced teeth can be easily chipped or broken. Also, misaligned or overlapping teeth are more difficult to brush which lead to gum disease and cavities.
How to prepare for an orthognathic surgery ?
Consultation with Specialists :
The first step in preparing for orthognathic surgery is to schedule a consultation with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and an orthodontist.
During this initial appointment, the surgical team will evaluate your dental and facial anatomy, discuss your treatment goals and expectations, and explain the surgical process in detail.
Comprehensive Evaluation :
A comprehensive evaluation, including dental and facial imaging (such as X-rays, CT scans, and/or MRI scans), will be conducted to assess the extent of the jaw misalignment and plan the surgical procedure accordingly.
This evaluation helps the surgical team develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Orthodontic Treatment :
Prior to surgery, you may undergo a period of pre-surgical orthodontic treatment to align the teeth and optimize the bite.
Orthodontic appliances, such as braces or aligners, may be used to move the teeth into the proper position and create a stable foundation for the surgical correction of the jaw alignment.
Medical Evaluation :
A thorough medical evaluation will be performed to assess your overall health and identify any underlying medical conditions that may affect your eligibility for surgery or increase the risk of complications.
This evaluation may include a review of your medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
Dental Preparation :
Prior to surgery, you may need to undergo dental procedures to address any existing dental issues, such as cavities or gum disease. It's essential to maintain good oral hygiene and address any dental concerns before undergoing orthognathic surgery to reduce the risk of post-operative complications.
Smoking and Alcohol Cessation :
If you smoke or regularly consume alcohol, it's important to quit or significantly reduce these habits before surgery.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can impair healing and increase the risk of complications during and after orthognathic surgery. Your surgical team may provide resources and support to help you quit smoking or reduce alcohol intake.
Medication Review :
Inform your surgical team about any medications you are currently taking, including prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and supplements. Some medications may need to be adjusted or discontinued before surgery to minimize the risk of bleeding or other complications.
Nutritional Counseling :
Proper nutrition is essential for optimal healing and recovery after orthognathic surgery. Your surgical team may provide nutritional counseling and dietary guidelines to ensure you are consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein before and after surgery. It may be helpful to stock up on soft foods and liquids for the post-operative period.
Support System :
Arrange for a support system to assist you during the recovery period following orthognathic surgery. This may include family members, friends, or caregivers who can provide emotional support, help with daily activities, and assist with transportation to and from medical appointments.
Pre-operative Instructions :
Follow any pre-operative instructions provided by your surgical team, such as fasting guidelines, medication instructions, and specific hygiene protocols. It's essential to adhere to these instructions to ensure a safe and successful surgical experience.
Orthodontics in Egypt :what are the different treatments and how are they performed ?
Orthodontic treatment Egypt depend on the degree of malocclusion of each patient, so you must have a consultation with your orthodontist to examine your teeth and evaluate your general health. Then, a diagnosis is realized through an X-ray of the teeth and a dental impression , so, he will suggest one or more of the following orthodontic treatments:
- Fixed braces
- Removable braces
- Retainers
- Oral surgery
Fixed braces :
To fit fixed braces, the dentist or orthodontist glues brackets to each tooth using cement. Arch wires are then attached to all the braces and are usually held in place with rubber bands or metal ties.
You may experience some temporary discomfort after the initial placement of the braces or during adjustment visits. Fixed braces take some time to get used to it and may cause discomfort to your lips and inner cheeks. If necessary, orthodontic wax can be applied to the braces.
To reduce the pain after the adjustment visits, it is recommended to eat soft foods.
Removable braces :
Although removable appliances are not as precise as fixed braces, they can still move one or more teeth. Fitted by your dentist or orthodontist, removable appliances can be worn before fixed braces are fitted, at the same time as fixed appliances or independently of them to treat specific problems.
Retainers :
Once fixed braces have been removed, a retainer can be used to keep your teeth in place. Retainers are either fixed (attached to the teeth) or removable. In some cases, they must be worn all the time, while in other cases, part of the day is sufficient.
Oral surgery :
Tooth extraction may be necessary if one or more teeth overlap or are in a very bad position.
When the size or position of the upper and lower jaws do not match at all, maxillofacial surgery (or orthognathic surgery) may be required. If your dentist or orthodontist feels that an operation is preferable, he or she will refer you to a specialist in oral and maxillofacial surgery.
Orthodontics in Egypt : aftercare and recovery
After your treatment of orthodontics in Egypt, you may feel a little discomfort during the first days, you will also have to eat soft foods.
This treatment lasts from 12 months to 27 months, it depends on the degree of malocclusion.
You must visit your orthodontist regularly for check ups.
Following the recommendations of your orthodontist is necessary.
Results
The results of orthodontics Egypt are excellent, but the patient must follow the advice of his orthodontist.
This treatment allows the patient to get rid of all problems related to chewing, articulation…and makes him regain self confidence by having a radiant smile and healthy teeth.
What are the risks of orthognathic surgery ?
Bleeding :
Bleeding is a common risk associated with any surgical procedure, including orthognathic surgery. While the surgical team takes precautions to minimize bleeding during the procedure, excessive bleeding can occur during or after surgery. In some cases, additional interventions may be required to control bleeding.
Infection :
Infection is another potential risk following orthognathic surgery. Despite strict sterile techniques and antibiotic prophylaxis, infections can occur at the surgical site or in the surrounding tissues. Symptoms of infection may include swelling, redness, warmth, and increased pain. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is necessary to prevent complications.

Nerve Damage :
Orthognathic surgery involves manipulation of the facial bones and adjacent nerves, which can sometimes result in nerve damage.
Nerve injuries may cause numbness, tingling, or altered sensation in the face, lips, or tongue. While most nerve injuries resolve spontaneously over time, some cases may require additional treatment or rehabilitation.
Relapse :
There is a risk of relapse following orthognathic surgery, particularly if proper post-operative care and follow-up are not maintained.
Relapse occurs when the corrected jaw position gradually returns to its original position over time. To minimize the risk of relapse, patients must adhere to post-operative instructions, wear prescribed orthodontic appliances, and attend regular follow-up appointments.
Malocclusion :
Malocclusion, or improper alignment of the teeth and jaws, is a potential complication of orthognathic surgery.
Despite careful planning and execution of the surgical procedure, discrepancies in the bite may occur, leading to issues such as difficulty chewing, speech problems, and dissatisfaction with the aesthetic outcome. Additional orthodontic treatment or revision surgery may be necessary to address malocclusion.

